The battery of an electric bike is like the heart of a human body, which is also the most valuable part of an e-Bike. It contributes largely to how well the bike performs. Even though with the same size and weight, the differences in structure and formation still be the reasons that batteries perform variously.
What we have seen the most popular types of battery nowadays are Lead-acid batteries and Lithium-ion batteries.
Get familiar with different battery types
Lead-acid battery

Since its early development in the 1950s, this has become the most applicable and widely used battery technology in history. Lead-acid batteries are commonly used in UPS, car batteries, etc.
The lead-acid battery has earned its reputation with good performance in high-temperature environments and abuse tolerance. Thanks to this feature, electric bikes that are equipped with lead-acid batteries are showing better performance on rough road conditions, with a lower battery maintenance rate.
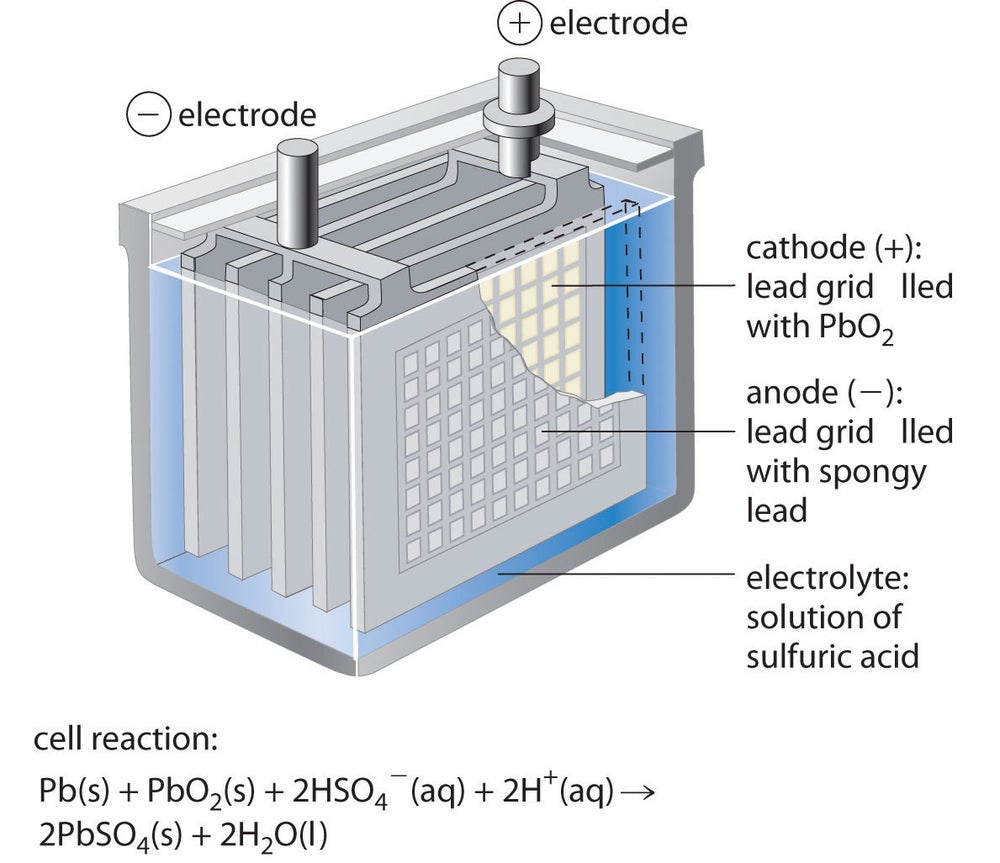
The acid contents can transfer the heat to the outside and are less likely to dry out, to maintain a proper working condition. It has around 500 charge cycles before it reaches the end of life. However, this structure keeps the battery relatively heavy and clumsy, which ends up with a higher weight of e-bike.
All types of battery have suffered from self-discharge issues, which means it loses juice even not being used. The lead-acid battery has a low self-discharge rate that allows it to output smoothly and steadily. On the other hand, a lead-acid battery requires an exceptional longer charging time of around 8-10 hours and its maximum capacity is only half that of a lithium-ion battery.
Lithium-ion battery

You may have seen a wide variety of lithium-ion battery forms that are commonly used by different electric bicycle brands and manufacturers. Lithium-ion is an excellent material for a fast-charging power supply with a much shorter charge time, flexibly smaller size, and longer life span than a lead-acid battery.
We have summarized some most commonly used lithium battery types from the Battery University.
Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (LiNiMnCoO2) —NMC
The recipe of NMC is to mix Nickel and Manganese. Nickel is famous for its high specific energy but awful stability; manganese has the advantage of forming a special structure to gain low internal resistance but delivers poor specific energy. Combining the metals helps minimize drawbacks and maximize the strengths of each other.

NMC has become the battery of choice for e-bikes, electric power tools, and powertrains. This offers lower raw material costs because of the reduction in consumption of expensive content cobalt.
The charging time is typically 3 hours with the ability to reach 1000-2000 cycles.
According to the American famous electric bike brand Super73, NMC also is the same type of battery that they used on all popular models.
After a great amount of research and testing, Tesla decided to choose NMC as its primary battery type and has developed the 18650 battery.
Comments:
Cost-effective, High capacity, High power
Lithium Iron Phosphate(LiFePO4) — LFP

Besides a high current rating and long cycle life, LFP also offers good thermal stability, enhanced safety, and abuse tolerance. With as many as 2000 cycle counts and a high thermal runaway temperature of 270°C, LFP out-performed other Lithium-ion batteries on application stability to be allegedly the safest one. LFP has a lower cost on manufacturing, given that it is often used as a replacement for the lead-acid battery.
It needs 3 hours to charge to its full capacity.
For portable and stationary needing high load currents and endurance, LFP is incontrovertible the best choice.
Comments:
High current rating, Long cycle life, Good thermal stability, Enhanced safety, Tolerance if abused;
Higher self-discharge, Low capacity
Lithium Cobalt Oxide(LiCoO2) — LCO
It is common to find Lithium Cobalt Oxide batteries in mobile phones, laptops, and digital cameras because of the high specific energy that LCO holds.
Compared to LEP, it is less stable due to the high sensitivity of temperature as the thermal runaway point is around 150°C (302°F).
In terms of the depth of discharge, load, and temperature, the LCO battery delivers charge cycles somewhere between 500-1000. That makes this type of battery have a relatively shorter life span.
It lacks specific power to carry a larger load capacity, which means it is not a perfect battery for bikes often carrying people or cargo.
Besides, 3 hours are needed for the battery to be fully charged.
Comments:
Very high specific energy;
Shorter life span, low thermal stability, Limited load capabilities (specific power), Kind of expensive
Lithium Manganese Oxide (LiMn2O4) — LMO

Its capacity is approximately two-thirds that of LCO.
The excellent flexibility on design enables manufacturers to use the best of either longevity, maximum load current (specific power), or high capacity (specific energy) in a battery. For instance, changing from the long-life version, the capacity can be increased from only 1,100mAh to 1,500mAh in high capacity version.
However, the LMO battery can only undergo 300-700 charging cycles due to the sensitivity on the depth of discharge and temperature.
Comments:
Fast charging;
High-current discharging, Less capacity
There are a few things that you need to know for keeping your e-bike battery in a good shape

Driving
For most batteries, hot and cold weather condition reduces performance. So avoid using e-bike during extreme temperatures in summer or winter days. Follow the instructions that are provided by your manufacturer.
Avoid bumpy grounds, potholes, speed bumps that will cause aggressive shock or vibration to the battery. The same principle applies when you handle a removable battery.
Charging
Avoid charging your unit immediately after driving.
Allow some time for the battery to cool down instead of keeping it at a high temperature. Vice versa, the same principle also applies when you are done charging.
Use the right charger or adaptor provided by the manufacturer. An unmatched charging unit may cause permanent damage to your battery.
Do not leave the charger plugged when done charging.
Storage
Elevated storage temperature, as well as frost, shortens the service life.
Do not store your battery outside where it may expose to heat, cold (below 0), moist.
Do not discharge below 20% of the capacity.
Before putting the battery into long-term storage, read carefully the user’s menu and follow the instructions recommended by the manufacturer.
Reference:
https://batteryuniversity.com/article/bu-205-types-of-lithium-ion
https://batteryuniversity.com/article/bu-402-what-is-c-rate
Post time: Dec-18-2021
